General Anesthesia and Sedation
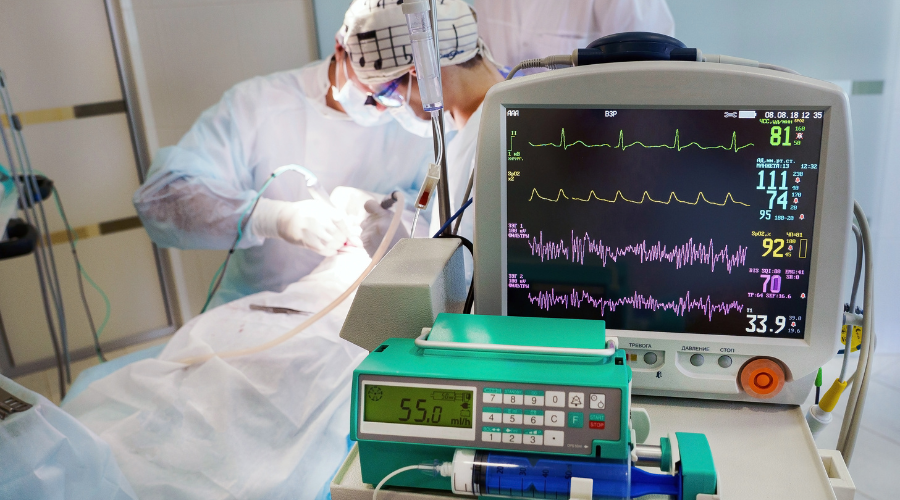
Understanding Sedation and General Anesthesia and Sedation in Dental Treatments, for individuals experiencing dental anxiety or difficulties during dental procedures, managing fear and anxiety is essential. This can be addressed through psychological methods and pharmacological interventions.
Effective Communication and Patient Management
Effective communication is pivotal in dental care. Nevertheless, when psychological strategies and standard behavior management techniques fall short, dental treatments become increasingly complex. In such cases, the use of is often necessary to facilitate the procedures.
The Role of Sedation in Dental Care
Sedation involves the reduction of a patient’s environmental awareness and a decrease in consciousness by suppressing the central nervous system. The primary aim of sedation is to reduce the psychological and physiological responses to stress while preserving consciousness and protective reflexes.

General Anesthesia in Dental Procedures
Through general anesthesia, consciousness is completely eliminated using pharmacological agents, placing the entire body under anesthesia’s influence. This method is crucial for patients who cannot undergo procedures with local anesthesia alone.
Typical Candidates for General Anesthesia and Sedation
Among those frequently benefiting are:
- Children with intellectual disabilities in need of dental care,
- Individuals, whether children or adults, with developmental delays,
- Adult patients experiencing significant dental anxiety,
- Procedures that require general anesthesia, such as bone grafting or cyst removal,
- Patients requiring multiple surgical interventions within a single session, which are not feasible with local anesthesia,
- Young children, particularly those under 4 years old, for whom traditional persuasion methods are often ineffective in dental settings.
In summary, when traditional methods are insufficient for managing dental treatment in patients with high anxiety or special needs, provide effective solutions, ensuring both safety and comfort during dental procedures.
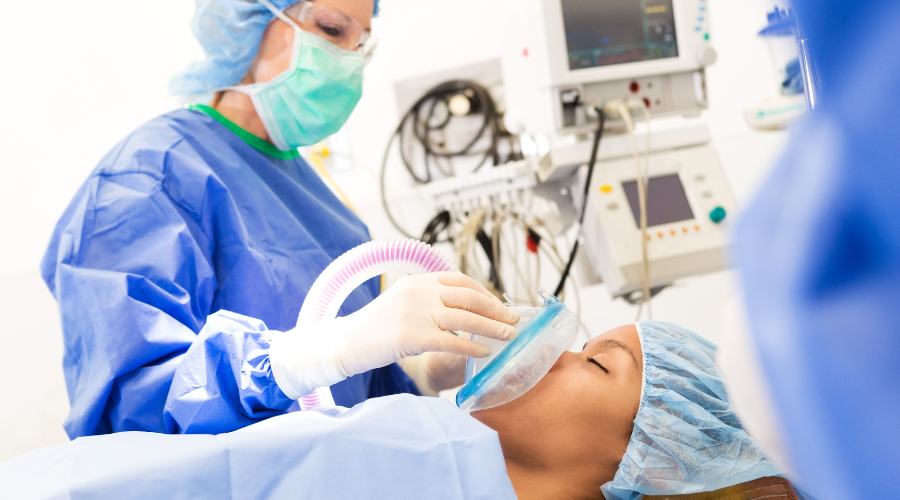
Preparing for Anesthesia or Sedation: What Patients Should Know
Preparation is key when it comes to anesthesia or sedation. It starts with a thorough preoperative assessment.
This assessment includes a review of your medical history and current medications. It may also involve certain tests to evaluate your health status.
Here are some important steps to prepare for anesthesia or sedation:
- Follow the fasting guidelines provided by your healthcare provider.
- Discuss any allergies or previous reactions to anesthesia.
- Arrange for a responsible adult to accompany you home after the procedure.
- Avoid smoking and alcohol as they can affect anesthesia outcomes.
By following these steps, you can help ensure a smooth procedure and recovery.
Recovery and Postoperative Care
Recovery from anesthesia or sedation varies among individuals. It depends on the type of anesthesia used and the individual’s overall health.
After the procedure, you may feel groggy or disoriented. This is a common side effect of anesthesia and should pass with time.
Here are some tips for postoperative care:
- Rest and take it easy for the first 24 hours.
- Follow your healthcare provider’s instructions regarding diet and medication.
- Report any unusual symptoms to your healthcare provider immediately.
Remember, proper postoperative care is crucial for a smooth recovery and minimizing potential complications.
Conclusion: The Importance of Informed Decisions in Anesthesia and Sedation
Understanding the differences between general anesthesia and sedation is crucial for informed decision-making. It helps patients and healthcare providers choose the best option for each procedure.
Remember, the goal is to ensure patient safety and comfort while achieving the best possible medical outcomes.